¿Qué es mejor implante o puente dental?
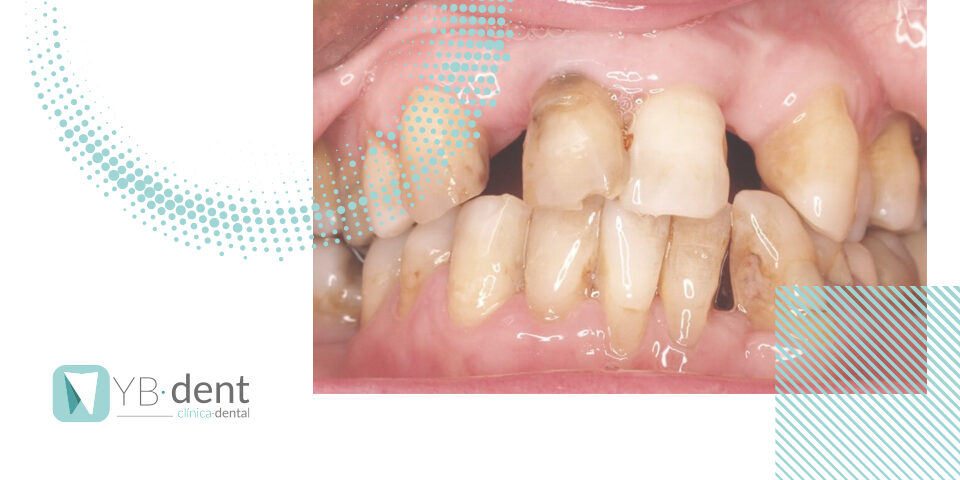
Uno de los peores miedos de nuestros pacientes es que algún problema les ocasione la pérdida de alguna pieza dental. Nosotros nos encargamos de evitar llegar a este punto, pero hay que saber que la pérdida de una pieza dental puede solucionarse con varios métodos y subsanar el problema.
Llegados a este punto nuestros pacientes se encuentran con dos opciones donde elegir
¿Qué es mejor el implante dental o el puente dental?
En la mayor parte de las ocasiones, esto dependerá de las necesidades y el caso concreto del paciente. Pero hoy te dejamos una breve explicación de cada una de estas opciones y en qué casos, suele utilizarse.
Los implantes
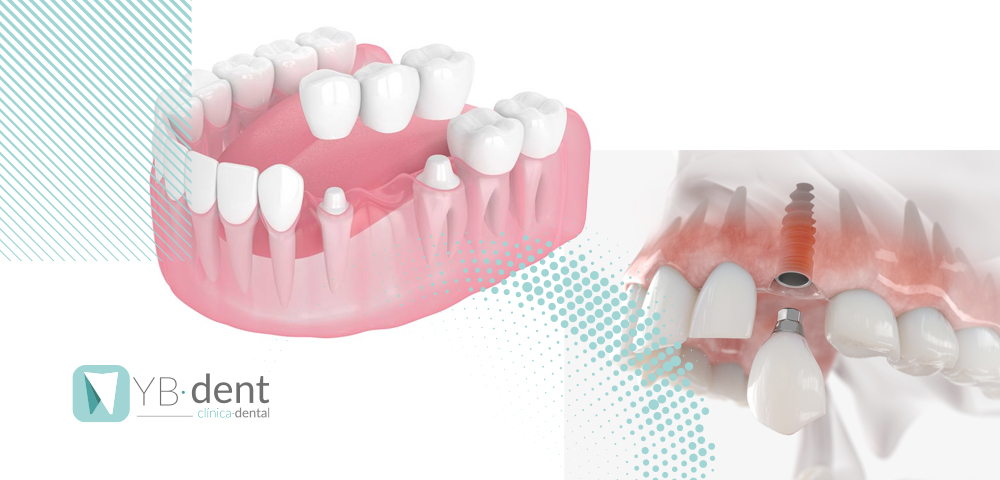
Son tornillos de titanio que se implementan en el hueso de la mandíbula, por lo que también se prescinde de la raíz del diente. Este tornillo se recubre por una corona, normalmente hecha de zirconio, metal o porcelana que simula el aspecto del diente y da la funcionalidad y la estética de este.
Los implantes tienen muchos argumentos a favor para nuestros pacientes:
- La estética se mantiene. Con los implantes se recupera la estética del diente original
- Es un trabajo individual de esta pieza dental, no necesita que otros dientes estén intervenidos en la recuperación.
- Durabilidad. Si por algo se caracterizan los implantes es porque con un cuidado adecuado, se pueden mantener de por vida.
- En muchos casos, la eliminación de la raíz repercute directamente en la mantención del hueso de la mandíbula.
- El uso es exactamente igual que un diente normal, incluso el paciente sentirá este implante como un diente propio.
Pero, algunos pacientes deciden no utilizar este método por alguno de estos contras:
- Es un método más costoso que el que veremos a continuación.
- Algunos pacientes no pueden realizar este procedimiento por afecciones anteriores o enfermedades que puedan agravarse.
- Es una intervención quirúrgica, que requiere una recuperación que requiera un tiempo de cuidados específicos, y muchos pacientes son reticentes a este tipo de intervenciones.
El puente dental
Por otro lado, el puente dental es una estructura que se fija a los dientes naturales, y une entre sí coronas que reponen estos dientes: la pieza que falta y los de alrededor que se han tenido que tallar para usar de pilares donde apoyar el puente.
Aunque este tipo de puentes suelen variar conforme las necesidades del paciente, normalmente la estructura se fija a estos dientes mediante cemento dental y se queda fija. Por lo que solo podrá ser removida por un dentista.
Este tipo de reemplazos de piezas dentales suele tener seguidores y detractores, por una parte, vamos a ver las principales características por las que la gente opta por el puente dental:
- Normalmente son más económicos que los implantes, por lo que en muchas ocasiones se eligen por su coste.
- El puente dental de funciones masticatorias y mejora la vida del paciente, además dan apariencia aproximada a un diente natural.
- La intervención para implantarlo en nuestra boca es mucho más sencilla, y no requiere de un proceso tan largo del que recuperarse.
Pero, por otro lado, también tiene argumentos en contra:
- Se necesita reemplazarlos cada cierto tiempo, no son tan resistentes como los implantes.
- Los puentes dentales requieren un mantenimiento y normalmente son más difíciles de limpiar que un diente natural, por lo que pueden aparecer problemas derivados de una higiene deficiente, en las encías o de caries.
- Después de la extracción de un diente suele venir una pérdida ósea, y este tipo de sustitución del diente no puede evitarlo y puede afectar a los dientes vecinos, en cambio el implante sí evita este problema.
Como hemos visto, la decisión a la hora de sustituir una pieza dental va ligada a muchas características y al caso concreto del paciente. La mejor forma de elegir una de estas dos opciones, es dejarse aconsejar por un profesional de confianza que entienda sobre la materia. Es por eso que en la clínica dental YB-dent tratamos de dar un diagnóstico personalizado a cada paciente acorde a su caso y a su situación personal.